Input & Output
Overview
This week's lab will cover the following:
- Using different Python data types.
- Converting between data types.
- Prompting users for input.
- Displaying output to a user.
Lecture Slides
Creating your Github Repo for Lab 1
Use the following link to set up a GitHub repository for Lab 1. Open your Lab 1 repository in GitHub Codespaces, and open the provided template lab1.py. Update the comment block with the appropriate information for name, date, and usage.
What is a Variable?
A variable is a named location in memory used to store a value. The value can change over the course of a script or program. Think similarly to algebra, where you assign x or y as an unknown value in an equation and solve for it. Unlike algebra, variables in programming are declared knowing how they're going to be used and what type of information will be stored in them. Python supports dynamic or static typed variables.
- Dynamic variables
- With dynamic typed variables, the program determines what type of data a variable contains based on the context it is used in.
- Static variables
- With static typed variables, you must declare a type when defining the variable. That variable can then only store that type of data. These are more secure in many ways, but a bit more difficult to deal with.
You will be using dynamic variables in this lab. It is recommended when using variables that you give them meaningful names that reflect the intended purpose. Python has no command for declaring a variable, the variable is created when you assign a value to it. This data (the variable's contents) can be a string, integer, decimal number, characters, etc. We will only be covering string and integer objects in this lab. You will learn and use other Python built-in data object types in future labs.
Create a variable called curYear with a value of the current year, using the following sample sample.
curYear=2024
Data Types
There are two data types you will be using this week. Strings and integers.
Prompt the user to enter their name and store it in the variable name using the following sample. It is useful to include a space at the end of your prompt, to make it more readable.
name=input("What is your name? ")
To do:
Repeat the steps to prompt the user to enter the year they were born. Store the input in the variable birthYear with the prompt "What year were you born? ".
Calculate their age
Use the following code to calculate the user's age by subtracting their birth year from the current year. Store the result in the variable age.
age=curYear-birthYear
Try to run your script. Don't forget to give it execute permissions, like you did in last week in the Preparation lab. It will fail, indicating an error! That is because you are trying to perform math on two string data types. In order to perform math with these variables, you will need to convert them to integers.
Converting Data types
Modify the line where you calculated the user's age and stored it in the variable age to convert the strings to integers using the following sample.
age=int(curYear)-int(birthYear)
Try running your script again. You should not recieve an error. You also won't recieve any output, as we have not added code to print a message to the user.
Displaying a message to the user
You can use the print function to display output to the user. You did this last week. You can use the , character to concatenate (join) strings. Use the following sample to print the message "Hello name you are age years old" using variable substitution.
print("Hello", name, "you are", age, "years old.")
Completing the Lab
Your script should produce output similar to the following. If it does not, go back and complete whatever you've missed.
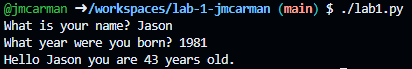
Upon completion of this lab you should have created a Python script with a variable containing the current year. Additionally, you should have prompted the user for their name and the year they were born, storing the information in variables. You converted the year strings to integers, performed simple math and displayed a message to the user. To submit your lab you need to submit the code to your GitHub repo (which you did in already in the lab).
Exploration Questions
The following questions are for furthering your knowledge only, and may appear on quizzes or tests at any time later in this course.
- What is a variable?
- Are variables in Python dynamically or statically typed?
- What type of data does a string contain?
- What type of data does an integer contain?
- What character do you use to concatenate or join strings?